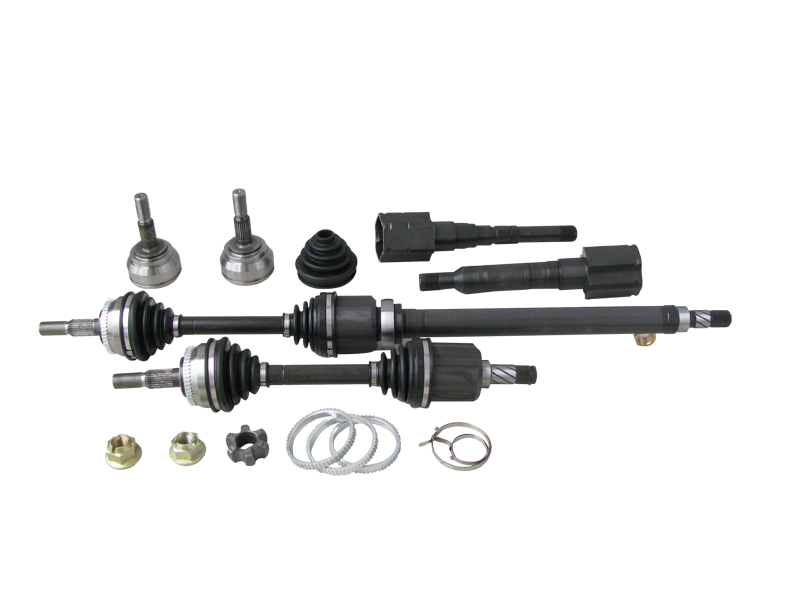
A Constant Velocity (CV) joint is a type of mechanical joint that plays a crucial role in the drivetrain of a vehicle. Its primary purpose is to connect the drive shaft to the wheels, allowing the efficient transmission of torque from the engine to the wheels. This setup is vital for enabling a smooth power transfer, especially as the wheels move up and down due to road surface changes and steer from side to side when the vehicle turns.

The design of the CV joint is engineered to provide a consistent rotational velocity regardless of the angle at which the drive shaft operates. This is particularly important because the drive shaft angle constantly changes. As the vehicle’s suspension compresses and extends over bumps, and as the wheels pivot left and right during steering, the CV joint accommodates these movements while maintaining uninterrupted power flow. Without this flexibility, the drivetrain would experience stress and binding, leading to premature wear and potential damage.
There are two main types of CV joints commonly used in vehicles today: the ball-type and the tripod-type. The ball-type CV joint is built with a spherical housing that contains a series of ball bearings. These bearings allow the joint to operate smoothly in multiple directions, providing excellent maneuverability for a wide range of angles. On the other hand, The tripod-type CV joint consists of three prongs (or “tripods”) that fit into matching slots within the joint housing. This configuration enables the joint to move up and down, as well as side to side, supporting a range of motions essential for effective wheel articulation.
Over time, CV joints undergo substantial stress due to their critical role in handling a vehicle’s suspension movements and steering angles. These joints can eventually wear out or become damaged, especially if exposed to dirt or road debris. Common symptoms of a worn or failing CV joint include clicking or popping sounds when making turns, noticeable vibrations during acceleration, and the appearance of grease around the joint area, often indicating a leaking CV boot. Since the CV boot (a protective rubber cover surrounding the joint) plays a crucial role in keeping grease in and contaminants out, a damaged or leaking boot can lead to accelerated joint wear.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the CV joint can help extend its service life. This typically involves periodically checking for signs of wear, ensuring the boot is intact, and replacing the joint grease when needed. By keeping the CV joint properly lubricated and free of contaminants, drivers can prevent premature wear, reduce repair costs, and ensure smoother, more reliable vehicle performance.