Suspension is the system of components, springs, shock absorbers and linkages that connects a vehicle to the wheels and tyres.
Suspension refers to the system of components in a vehicle that connects the wheels to the chassis and provides a smooth, comfortable ride while also maintaining the vehicle’s stability and handling characteristics . The suspension system is responsible for absorbing the impact of bumps and uneven road surfaces, while also maintaining the tire’s contact with the road.
The suspension system typically includes several components , such as springs, shock absorbers, struts
- The springs in the suspension system absorb the shock and provide a cushioning effect to the vehicle’s wheels. There are different types of springs used in suspension systems, including coil springs, leaf springs, and air springs.
- The shock absorbers or dampers in the suspension system work together with the springs to control the bouncing of the vehicle and to maintain its stability. Shock absorbers convert the energy of the spring’s movement into heat, which is dissipated into the atmosphere.
- Struts are a type of suspension component that combines the functions of the shock absorber and the spring. They are used in many modern suspension systems and offer several advantages over traditional shock absorber and spring setups, including better handling and improved ride comfort.
- Control arms are used to connect the suspension system to the chassis and to control the motion of the wheels. They are typically made of strong, lightweight materials such as aluminum or steel.
- Ball joints are used to allow the wheels to move in different directions while still remaining attached to the suspension system. They are typically used in conjunction with the control arms and are important for maintaining the stability and handling of the vehicle.
- Stabilizer bars, also known as sway bars, are used to reduce body roll and improve handling. They connect the suspension system of each wheel to the opposite side of the vehicle and transfer forces between the wheels, helping to keep the vehicle stable during cornering.
In summary, the suspension system is a complex system of components that work together to provide a smooth, comfortable ride while also maintaining the vehicle’s stability and handling characteristics .
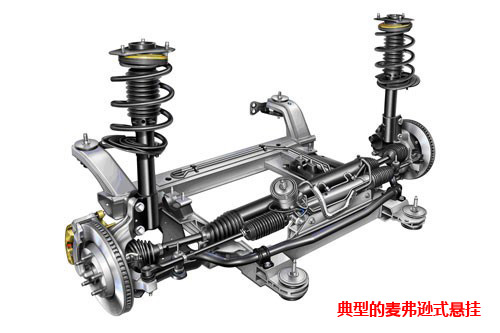
MacPherson strut Suspension
double-wishbone suspension / A-arm suspension


Double-wishbone suspension on Honda Accord 2005 Coupe
How Suspensions Work
hey car guy my one question is im tirnyg to do this on a? 2001 grand prix and my control arm is a little different meaning the screw nut is topside instead of bottom and i unscrewed the nut and hit knuckle with hammer but arm still tight what do you think it is?
Link | October 16th, 2015 at 3:46 am
I need cv joint Hyundai and Kia
Link | February 13th, 2022 at 7:11 am